
Resistors are used to control the flow of current in a circuit. They can be used to create voltage dividers, current limiters, and filters.
Capacitors are used to store electrical energy. They can be used to smooth out current fluctuations, create timing circuits, and filter noise.
Inductors are used to store magnetic energy. They can be used to create filters, oscillators, and transformers.
Diodes are used to allow current to flow in one direction only. They can be used to create rectifiers, clippers, and switches.
Transistors are used to amplify or switch electronic signals. They are the basic building blocks of most modern electronic devices.
Integrated circuits (ICs) are complex circuits that are built on a single semiconductor chip. They can contain millions of transistors and other components. ICs are used in a wide variety of electronic devices, including computers, smartphones, and TVs.
A moving coil galvanometer is a type of electrical instrument that measures electric current. It consists of a coil of wire suspended in a magnetic field. When a current flows through the coil, it generates a force that deflects the coil. The amount of deflection is proportional to the current flowing through the coil.

An ammeter is a type of electrical instrument that measures electric current. It is connected in series with the circuit that is being measured. The ammeter has a very low resistance, so it does not significantly affect the current in the circuit.

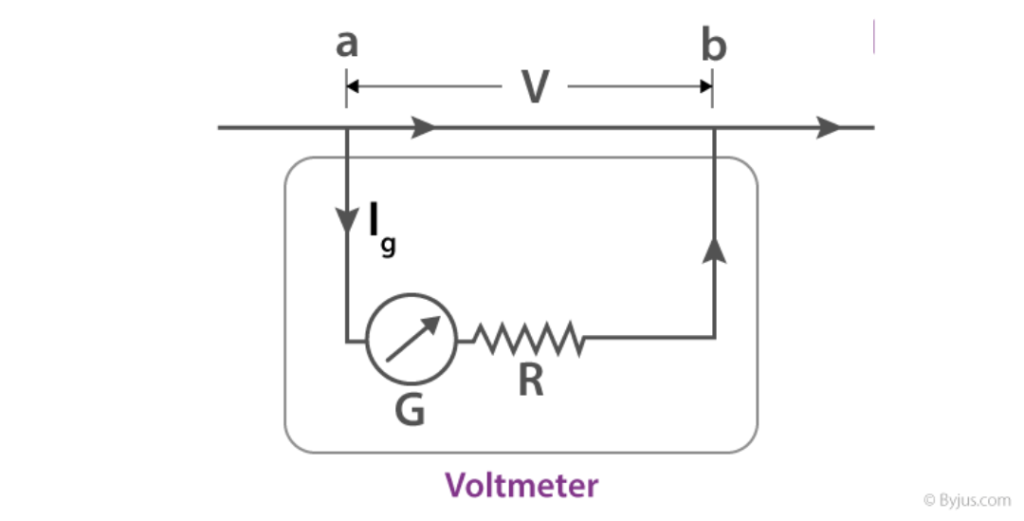
A voltmeter is a type of electrical instrument that measures electric potential difference. It is connected in parallel with the circuit that is being measured. The voltmeter has a very high resistance, so it does not significantly draw current from the circuit.
Here is a table that summarizes the key differences between moving coil galvanometer, ammeter, and voltmeter:
| Feature | Moving coil galvanometer | Ammeter | Voltmeter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type of instrument | Electrical | Electrical | Electrical |
| Measures | Electric current | Electric current | Electric potential difference |
| Connection to circuit | Series | Series | Parallel |
| Resistance | Low | Very low | Very high |
| Effect on circuit | Affects current | Does not affect current | Does not affect current |
Electricity is a powerful force that can be dangerous if not handled properly. The hazards of electricity include electric shock, fire, and explosion.
Electrical insulation is the material that surrounds electrical wires and cables. It protects the wires from coming into contact with each other and from coming into contact with people or other objects. Damaged insulation can expose the wires and make them susceptible to electric shock.
Series combinations are useful when specific voltage drops are required or when using multiple resistors to achieve a desired total resistance. However, the increase in total resistance can impact overall circuit performance.
Overhead cables are electrical cables that are suspended above the ground. They are often used to transmit electricity over long distances. Overhead cables can be a hazard if they come into contact with trees or other objects, or if they are damaged by weather or other events.
Damp conditions can increase the risk of electric shock. This is because water is a conductor of electricity. If electrical wires or cables come into contact with water, they can create a shock hazard.
There are a number of safety measures that can be taken to reduce the risk of electrical accidents in the home. These include:
Fuses and breakers are safety devices that are used to protect electrical circuits from overloads and short circuits. Fuses are designed to melt and break the circuit if the current exceeds a certain level. Breakers are designed to trip and open the circuit if the current exceeds a certain level.
A circuit breaker is an electrical safety device that is used to protect electrical circuits from overloads and short circuits. When a circuit breaker trips, it opens the circuit and stops the flow of electricity. Circuit breakers are typically installed in the home’s electrical panel.
A ground wire is a safety wire that is connected to the earth. It is used to protect people from electric shock in the event of a fault in the electrical system. The ground wire provides a path for the current to flow to the earth, rather than through a person. Ground wires are typically installed in the home’s electrical system.
Parallel combinations are useful when maintaining voltage consistency is important or when multiple resistors need to achieve a lower total resistance. However, complex calculations and potential variations in voltage distribution should be considered.
Electric shock can cause the heart to stop beating. This is called cardiac arrest. Cardiac arrest is a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention.
Electric shock can also cause respiratory arrest. Respiratory arrest is when a person stops breathing. Respiratory arrest is also a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention.
Electric shock can cause burns on the skin. The severity of the burns will depend on the amount of current that flows through the body and the length of time that the current flows.
Electric shock can cause muscle contractions. These contractions can be so strong that they can throw a person off their feet or cause them to lose control of their body.
Electric shock can cause neurological damage. This damage can range from temporary confusion to permanent disability.

0 of 23 Questions completed
Questions:
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
0 of 23 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
What is the main purpose of a diode in a circuit?
What is the function of a moving coil galvanometer?
Which instrument is connected in series with the circuit it measures?
What is the primary hazard associated with electricity?
What is the primary purpose of using fuses and breakers in household electricity?
How does a voltmeter affect the circuit it is connected to?
What is the role of insulation in electrical wires and cables?
Which safety measure helps reduce the risk of electric shock in damp conditions?
How does a resistor affect the flow of current in a circuit?
To measure electric potential difference
What is the main principle behind electromagnetic induction?
What law states that a changing magnetic field induces an electromotive force in a closed loop?
What factors affect the magnitude of induced electromotive force (EMF)?
According to Lenz’s Law, what is the relationship between the induced electromotive force (EMF) and the change in magnetic flux?
How does Lenz’s Law contribute to the conservation of energy in electromagnetic systems?
What is the main purpose of a diode in a circuit?
What is the function of a moving coil galvanometer?
Which instrument is connected in series with the circuit it measures?
What is the primary hazard associated with electricity?
What is the primary purpose of using fuses and breakers in household electricity?
How does a voltmeter affect the circuit it is connected to?
What is the role of insulation in electrical wires and cables?
Which safety measure helps reduce the risk of electric shock in damp conditions?