
Light signals are transmitted through optical fibers using a process called optical communication, which involves sending light pulses through thin strands of glass or plastic fibers. Here’s how the process works:
The origin point generating intense light pulses for transmission.
The process of modulating light pulses to encode information.
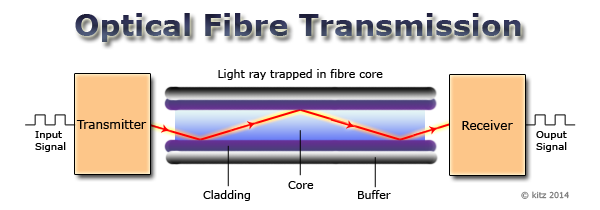
Introduction of modulated light pulses into the core of an optical fiber.
Phenomenon where light repeatedly bounces within the core of the optical fiber due to refractive index differences.
Travel of light pulses through the fiber via total internal reflection.
Loss of signal strength and slight separation of different wavelengths due to scattering and other factors.
Detection of light pulses at the receiving end and extraction of original information through demodulation.
Strengthening of received signal and reduction of noise or distortions through processing.
Utilization of the processed signal for various applications such as sound reproduction or data display.

0 of 12 Questions completed
Questions:
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
0 of 12 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
What happens to electrons when subjected to a magnetic field perpendicular to their motion?
What force causes electrons to follow a curved trajectory in a magnetic field?
In what direction do electrons deflect when subjected to a magnetic field?
How does the strength of the magnetic field impact the curvature of the electron’s path?
What is the relationship between the velocity of electrons and their deflection in a magnetic field?
When does an electron move in a circular path in a magnetic field?
What is the primary function of a Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (CRO)?
How is the electron beam in a CRO produced?
Which component of a CRO controls the horizontal movement of the electron beam?
What does the waveform trace on a CRO display represent?
What is the purpose of the trigger circuits in a CRO?
In what applications are Cathode Ray Oscilloscopes (CROs) commonly used?