
The process of transmitting electrical signals through wires involves the movement of electrons within the wire to convey information or power. Here’s a simplified explanation of the process:
The origin point generating an electrical signal, often voltage or current.
The process of representing information using variations in voltage or current.
The motion of electrons within a wire due to an applied electric field.
The slow net speed at which electrons move in a wire due to their random motion and collisions.
The transmission of the electrical signal along the wire through a chain reaction of electron movements.
The reduction in signal strength due to resistance and heat generation within the wire.
External factors causing distortion in the transmitted signal, including electromagnetic interference and noise.
The process of detecting, amplifying, and processing the transmitted signal for information recovery.
Utilizing the processed signal for various purposes such as display, sound production, or control of devices.
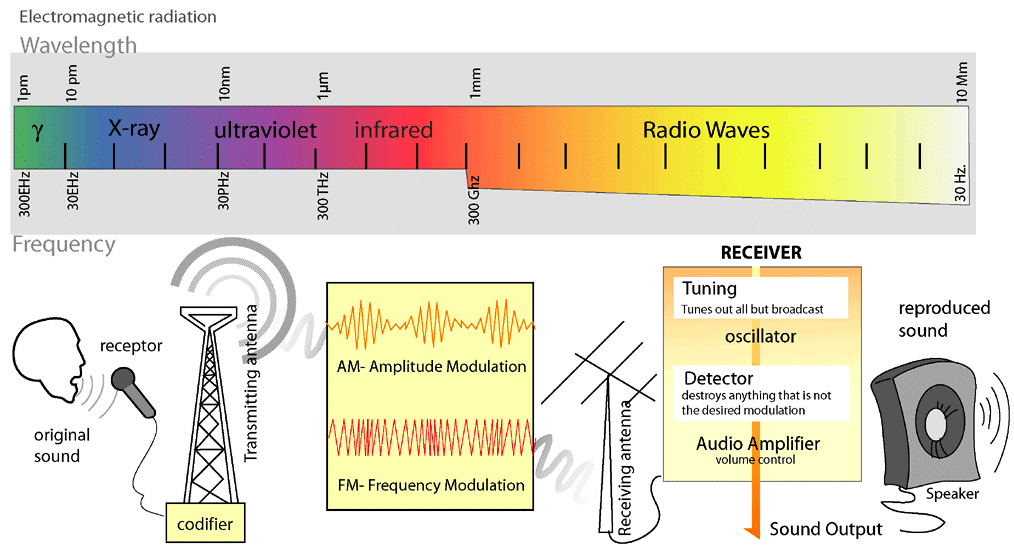
The process of transmitting radio waves through space involves the propagation of electromagnetic waves, specifically radio frequency (RF) waves. Here’s a simplified explanation of how this process works:
Certainly, here are the headings defined in one line each:
Creation of alternating current at a specific frequency.
Variation of radio wave properties to encode information.
Conversion of electrical signal to electromagnetic wave by the antenna.
Release of electromagnetic waves (radio waves) into the environment.
Travel of radio waves through the vacuum of space or atmosphere.
Course alteration due to obstructions and Earth’s curvature.
Capture of incoming radio waves by a receiving antenna.
Extraction of original information by reversing modulation.
Strengthening and refining of the received signal.
Utilization of processed signal for sound, display, or other applications.
A fax machine transmits images as electrical signals over phone lines. It encodes images, sends them as audio tones, and at the other end, decodes and prints the received image.
A cell phone emits radio signals encoding voice and data, which travel to a tower. The tower relays these signals, allowing the receiving phone to decode and display them.
The photophone conveys sound by changing light intensity with sound waves. The light carries the encoded sound, which is turned back into sound at the receiver.

0 of 10 Questions completed
Questions:
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
0 of 10 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
What distinguishes high-tech electric appliances from low-tech electrical appliances?
Which type of light source characterizes high-tech electric appliances?
What feature distinguishes digital thermostats from analog thermostats?
Which advancement allows smart appliances to communicate, provide notifications, and optimize energy use?
What is a key characteristic of smart home automation in high-tech electric appliances?
What is the main purpose of a diode in a circuit?
What is the function of a moving coil galvanometer?
Which instrument is connected in series with the circuit it measures?
What is the primary hazard associated with electricity?
What is the primary purpose of using fuses and breakers in household electricity?