
A group of similar types of cells organized together in a group is called tissue.
Animals are made up of four basic types of tissues
Epithelial tissue covers the surface of the body, lines the space inside the body and forms glands.
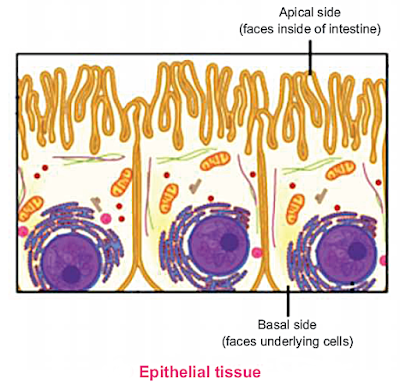
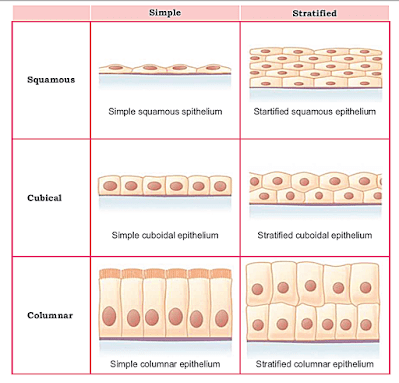
The simplest classification of these tissues is based on the number of cell layers.
When the epithelium is composed of a single layer of cells, it is called simple epithelial tissue.
Simple epithelial tissue can be classified into the following three types.
Stratified epithelium consists of more than one layer of cells and only one layer is in direct contact with the basement membrane.
Stratified epithelial tissue can be classified into following types
Stratified cuboidal epithelia are found surrounding the ducts of many glands, including mammary glands in the breast and salivary glands in the mouth.
Stratified columnar epithelia are rare, found predominantly in some organs of the reproductive system.
Transitional epithelia are a special subset of stratified epithelia. They are exclusively found in the excretory system.
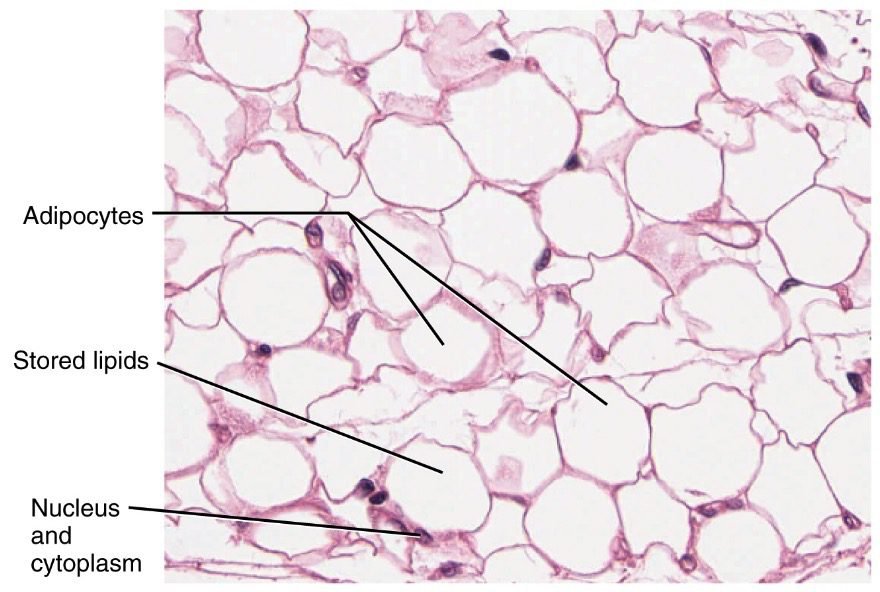
The tissue which connects or binds the different types of cells called connective tissues.These are made up cells,fibers and a gel-like substance.these tissues are widely found through the body between tissue and organs and also form sheaths around the organs.
Connective tissues serve many purposes in the body

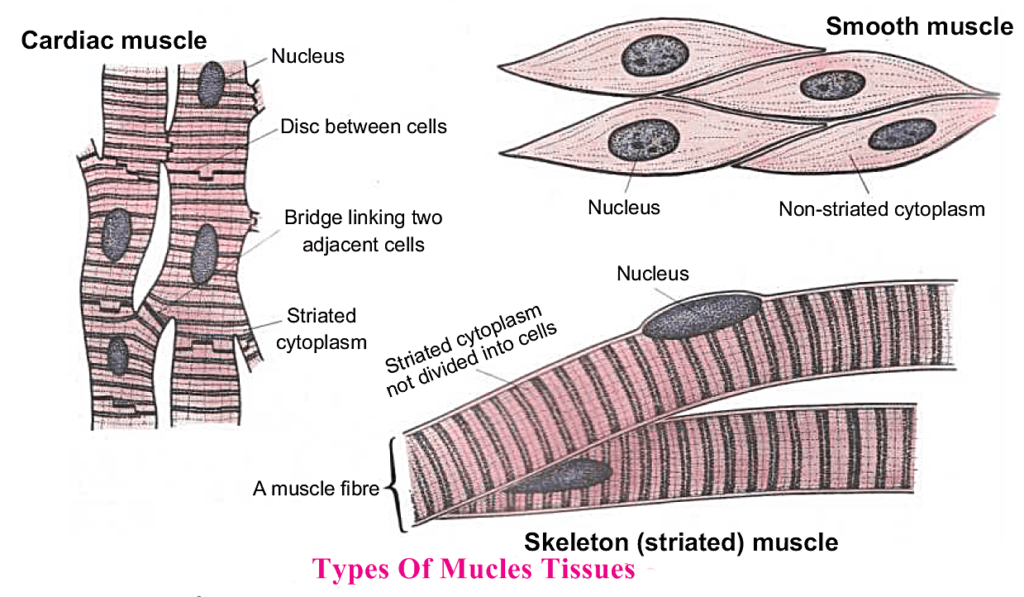
This tissue consists of muscle fibres.Each fiber consists of elongated cells containing nucleus Functions.
They are the following types of muscle tissues.
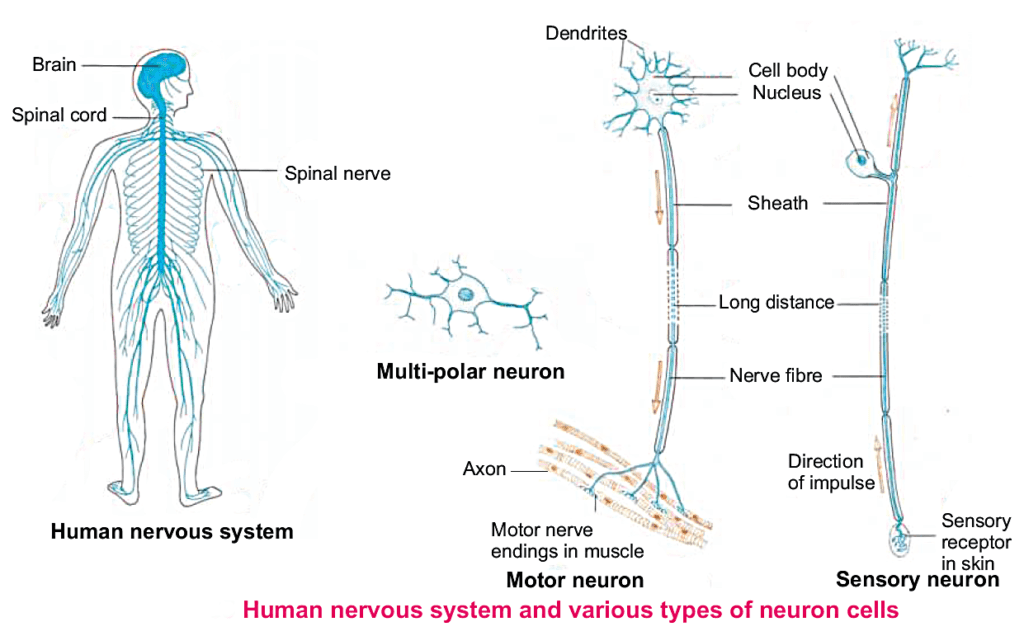
Nervous tissues consist of nerve cells called neurons or nerve cell.Each nerve cell is specialized cell consisting of three parts.Nervous system consisting of nervous tissues.

0 of 10 Questions completed
Questions:
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
0 of 10 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
What is tissue?
Which of the following is not a type of animal tissue?
Where is epithelial tissue found in the body?
What is the function of simple squamous epithelium?
Which type of epithelial tissue is found in the digestive tract?
What is the main function of connective tissue?
Which connective tissue is responsible for storing energy in the form of fat?
Which type of muscle tissue is voluntary and attached to bones?
What is the main function of nervous tissue?
What is the specialized cell in nervous tissue called?