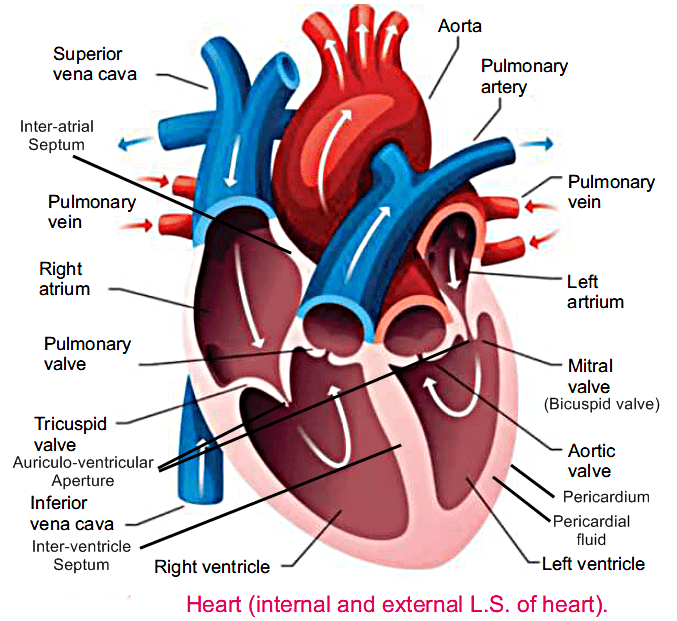
Heart is a muscular, pumping organ, It is located in the thorax. It is enclosed in a fibrous bag-like protective cover called pericardium. Externally it is conical in shape. Internally it consists of four chambers.
1) Upper two chambers are thin walled atria while the lower two are thick walled ventricles.
2) Atria are completely separated from each other by an interatrial septum.
3) Ventricles are separated by a muscular partition called inter ventricular septum.
4) An auricular-ventricular aperture connects each atrium with the ventricle of its own side.
5) In between the right atrium and right ventricle lies a tricuspid valve.
6) Similarly a bicuspid valve guards the opening between the left atrium and left ventricle.
7) These valves prevent the backflow of blood from the ventricles to the atria.
8) Two atria contract to flow the blood into ventricles which simultaneously push the blood into the body.
9) The blood from the right ventricle is pumped through the pulmonary area of the lungs for oxygenation while blood from the left ventricle is pumped through the aorta to all parts of the body.
The circulation of blood in our body is called double circuit circulation because it
circulates in two separate circuits.
1) Pulmonary circuit
2) Systemic circuit
This entire circuit i.e. blood from the lungs to heart and heat to lungs is called pulmonary circuit.
It is responsible to supply oxygenated blood to all parts of body except lungs through
systemic arch or aorta. This is called a systemic circuit. Initially, the aorta gives off three
branches which supply blood to the head, arms and shoulders. The aorta then descends down and
gives off many branches which supply blood to their respective organs e.g.
blood is collected from all organs by the blood vessels called veins e.g.
All these veins from posterior part of the body fuse together to form posterior vena cava. The veins from all the organs anterior to heart i.e. head and forelimbs fuse to form anterior vena cava.
Both anterior and posterior vena cava discharge all the venous blood into the right atrium from
where through right ventricle it is pumped to lungs through pulmonary circuit for oxygenation

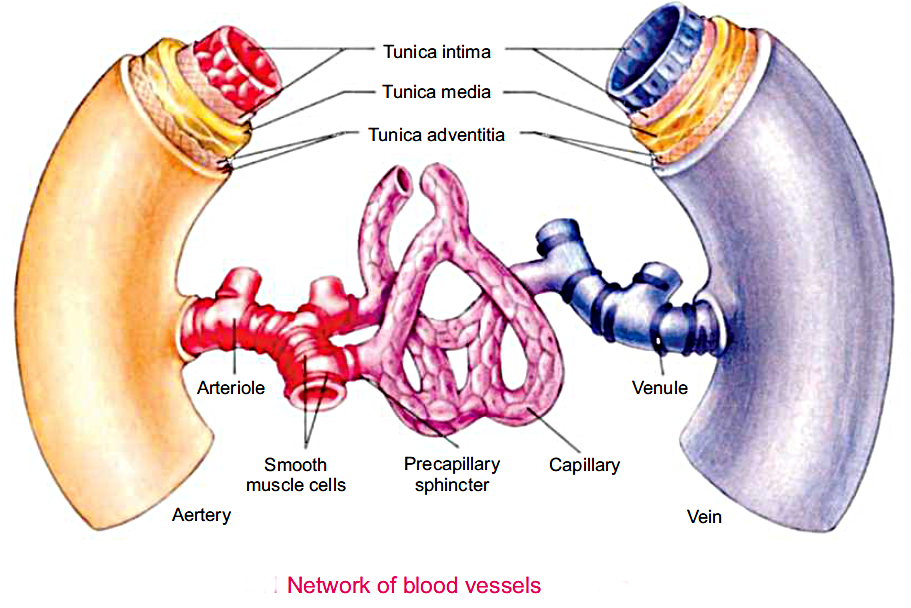
The blood vessels that carry blood from heart to various organs of the body are termed as arteries.
They are thick walled and more elastic than veins. Due to their thick walls, their inner space or lumen is narrower. They lie deep in the body. When an enters in corresponding organ it divides up into smaller branches called arterioles. The arteriole eventually divides into a fine microscope interconnected network of capillaries.
The wall of an artery is composed of three layers.
iii. An outer layer of elastic fibres and connective tissue.
There are microscopic vessels where exchange of various substances occurs between blood and the surrounding tissues.
Each capillary is composed of only single cell layers of endothelial cells.Internally, its diameter is slightly larger than that of a R.B.C.They are connected with arterioles on one side and vessels on the other side.
Veins are the blood vessels that bring blood back to heart. They are formed by the union of smaller branches called venules which in turn are formed by the fusion of capillaries with each other. The blood flow in a vein is slower and uniform as composed to the artery.
Veins are thin walled and less elastic than arteries. The walls of a vein are also composed of the same three but less muscular layers.
| Arteries | Veins |
|---|---|
| Arteries are the blood vessels that carry blood from heart to various organs of the body. | Veins are the blood vessels that bring blood back from various organs to the heart. |
| Arteries are thick walled and more elastic. | Veins are thin walled and less elastic. |
| The walls of arteries are more muscular. | The walls of veins are less muscular. |
| They lie deep in the body. | They do not lie deep in the body. |
| Arteries divide up into small branches called arterioles. | Veins divide up into small branches called venules. |

0 of 6 Questions completed
Questions:
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
0 of 6 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Which of the following is NOT one of the chambers of the human heart?
What is the function of the interatrial septum?
Which valve guards the opening between the right atrium and right ventricle?
Where does the pulmonary circuit carry deoxygenated blood?
Which of the following vessels supply blood to the head, arms, and shoulders?
What is the main difference between arteries and veins?