
A typical plant and animal cell consists of the following parts.
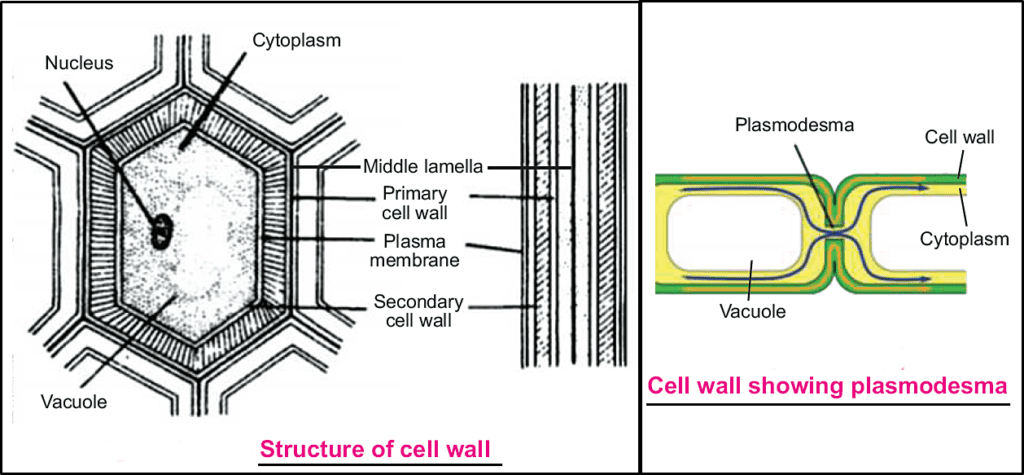
Cell wall is the outermost boundary of plant cells, bacterial cells and fungal cells. It is not found in animal cells.
i. Middle lamella
ii. Primary wall
iii. Secondary wall
Middle lamella is formed between the primary walls of two neighboring cells, It is a cementing layer between two cells.
Primary wall is the first wall of the plant cell. Chemically it is composed of cellulose and pectin sometimes, lignin.
Secondary wall is formed by deposition of cellulose at the inside of the primary wall.

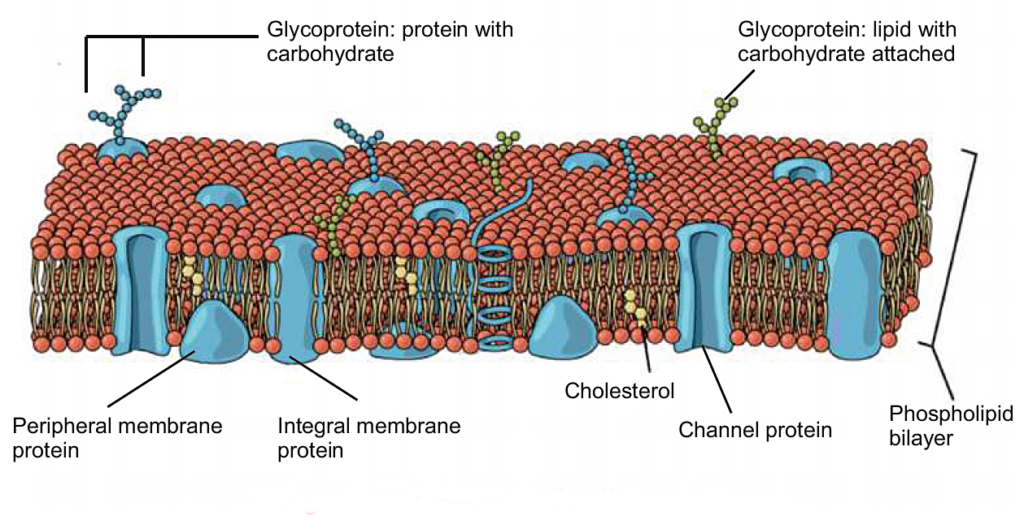
The cell membrane is the outermost living boundary of all cells.
The cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane, physically separates the intracellular space (inside the cell) from the extracellular environment (outside the cell). The cell membrane surrounds and protects the cytoplasm.


0 of 10 Questions completed
Questions:
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
0 of 10 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Which of the following cells have a cell wall?
What is the main component of the plant cell wall?
Which layer of the cell wall is formed between two neighboring plant cells?
What is the function of the cell wall?
Which term is used to describe the outermost living boundary of all cells?
What is the function of the cell membrane?
According to the fluid-mosaic model, the cell membrane is composed of:
Which process allows the movement of substances in and out of the cell through the cell membrane?
The cell membrane is selectively permeable to:
What important functions does the cell membrane perform for cells?