
Reflection of light is the bouncing back of light rays when they encounter a surface, obeying the laws of reflection and resulting in the formation of images.
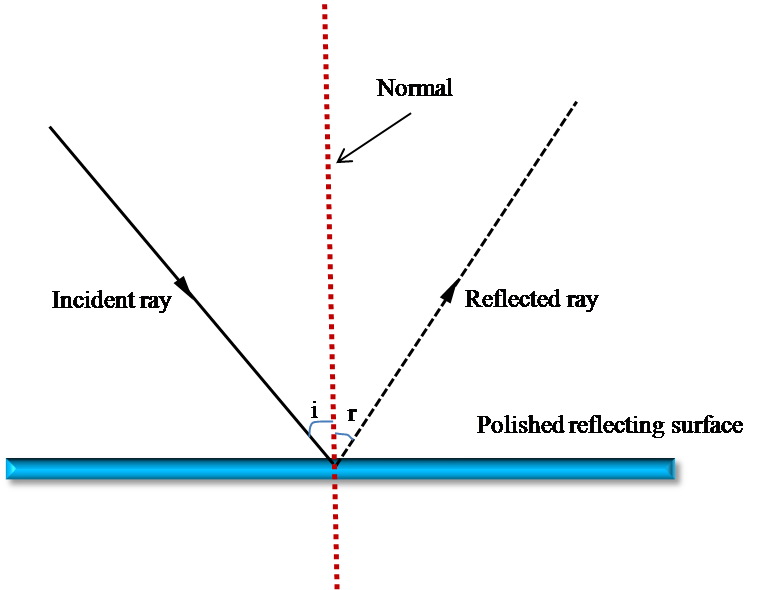
The first law of reflection states that the incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal (perpendicular line) to the reflecting surface all lie in the same plane.
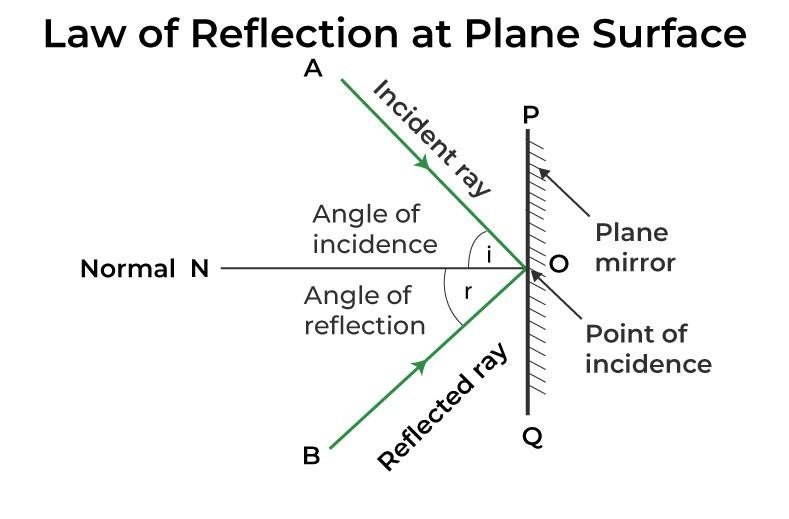
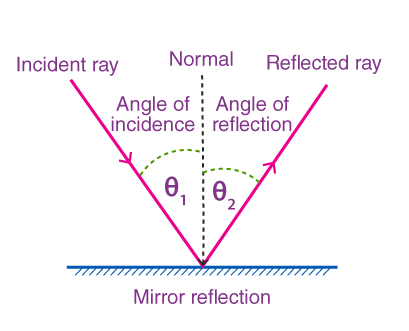
The second law of reflection states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection, measured between the incident ray and the normal compared to the reflected ray and the normal.
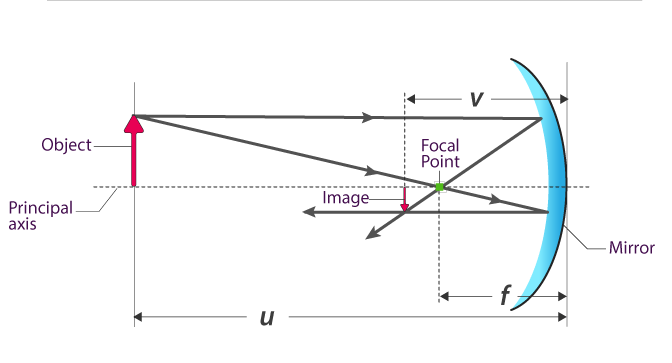
Spherical mirrors, whether concave or convex, create images through the reflection of light rays. The process varies based on the type of mirror:
| Object Position | Image Position | Image Size | Nature of Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beyond C | Between C and F | Reduced | Real, Inverted |
| At C | At C | Same as Object | Real, Inverted |
| Between C and F | Beyond C | Enlarged | Real, Inverted |
| At F | No real image | No real image | No real image |
| Between F and Mirror | Virtual | Enlarged | Virtual, Upright |
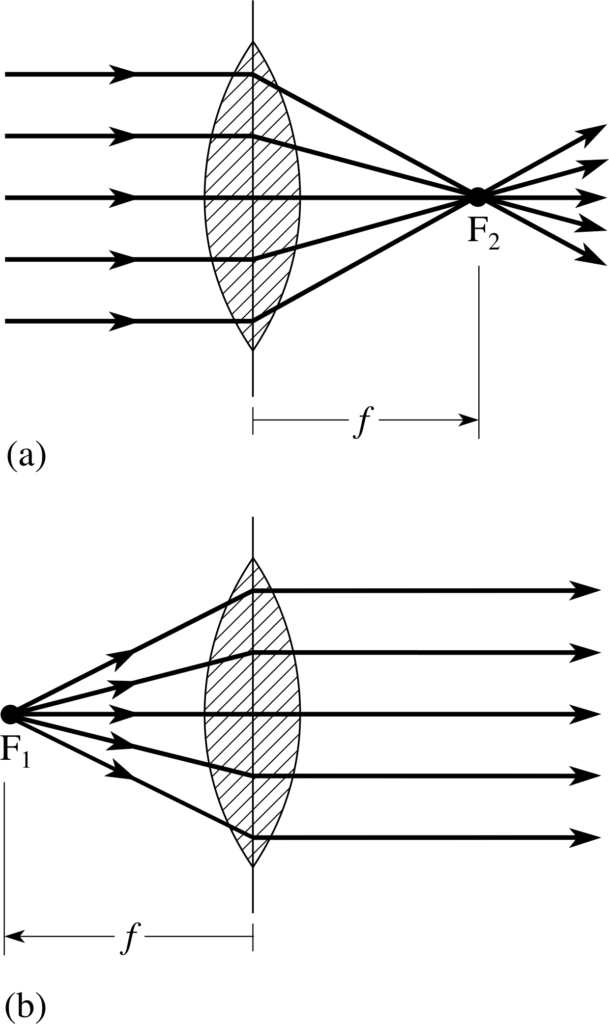
The spherical mirror equation is a mathematical relationship that relates the focal length (f), the object distance (do), and the image distance (di) for spherical mirrors. It helps determine the position and characteristics of the image formed by the mirror.
The spherical mirror equation can be expressed as:
\begin{equation} \frac{1}{f} = \frac{1}{d_o} + \frac{1}{d_i} \end{equation}
Where,
(f) = focal length of the mirror
(do) = object distance (distance of the object from the mirror’s pole)
(di) = image distance (distance of the image from the mirror’s pole)
Convex mirrors have several practical uses due to their unique reflective properties, such as the fact that they always produce virtual, upright, and diminished images. Some common applications include:
Convex mirrors play a crucial role in improving safety, visibility, and surveillance across various environments, making them valuable tools in everyday life.

0 of 18 Questions completed
Questions:
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
0 of 18 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
What happens when you rub a balloon on your hair?
Which type of electric charge is associated with an excess of protons?
How does a negatively charged balloon interact with neutral objects?
What is induction in the context of electric charge?
How does friction contribute to the formation of electric charge?
What happens when a positively charged metal sphere is touched with a neutral metal rod?
What happens when you rub a balloon on your hair?
Which type of electric charge is associated with an excess of protons?
How does a negatively charged balloon interact with neutral objects?
What is induction in the context of electric charge?
How does friction contribute to the formation of electric charge?
What happens when a positively charged metal sphere is touched with a neutral metal rod?
What is the primary function of an electroscope?
Which part of an electroscope acts as a terminal?
What materials are commonly used for the leaves in an electroscope?
How does an electroscope indicate the presence of a charge?
What causes the leaves of an electroscope to separate?
When an electrically charged object is brought near the electroscope’s metal knob, what initial process occurs?