
The kinetic molecular theory explains the behaviour of gases such as Diffusion, Effusion, Pressure, compressibility, Mobility and Density which are defined below;
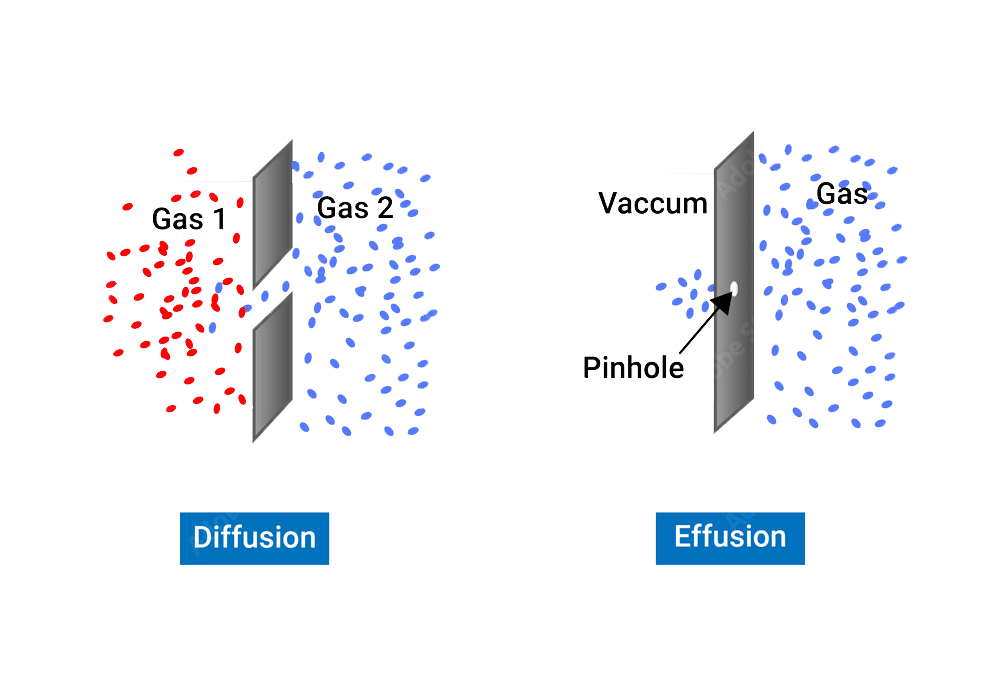
Diffusion is the process by which particles move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. It is a fundamental process in science that occurs in many different contexts, such as in gases, liquids, and solids.
There are many examples of diffusion that occur in our everyday lives. Here are some common examples:

Effusion is the process by which a gas or a substance in a gaseous state escapes through a small opening or a porous material. This can happen due to the difference in pressure between the two sides of the opening or material, causing the gas or substance to move from an area of high pressure to an area of low pressure. The rate of effusion depends on the size of the opening or material, the pressure difference, and the molecular weight of the gas or substance.
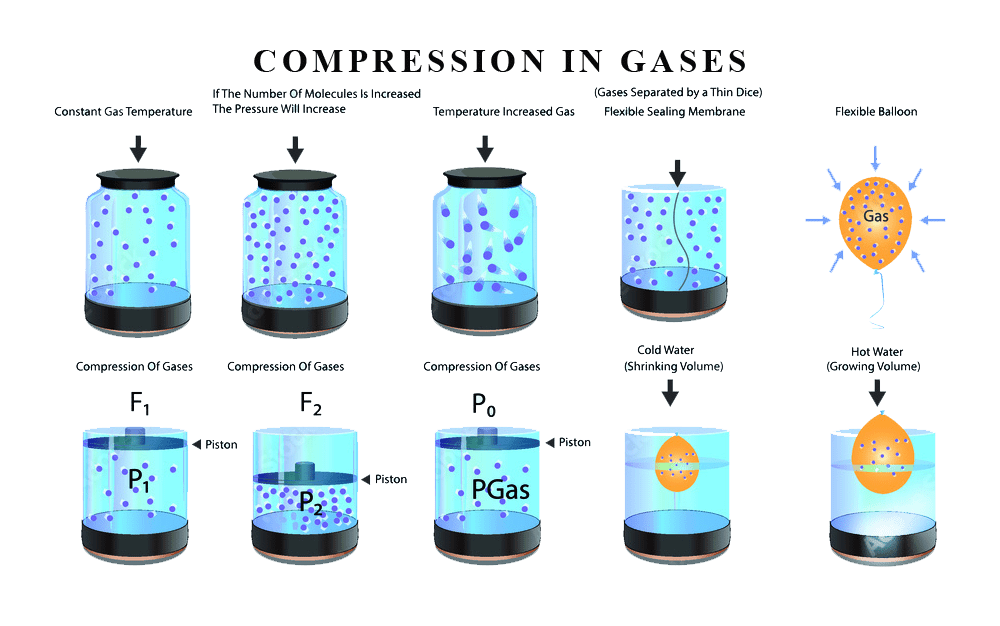
The force exerted by gaseous particles per unit area is called gas pressure. It can be expressed mathematically as.
Pressure =Force/Area
P = F/A = M/m2
The S.I unit of force is Newton (N) and unit of area is m2, hence pressure has S.I unit of S.I unit of Nm-2. It is also known as Pascal (Pa). 1 Pascal =1 Nm-2. .
Compressibility is a measure of how much the volume of a substance decreases when subjected to an applied pressure.
Mobility refers to the ability to move or be moved from one place to another. In the context of transportation, mobility often refers to the ease with which people or goods can travel between different locations. For example, a person who can walk or bike to school has more mobility than someone who must rely on a car or public transportation. In general, the term mobility can be used to describe the movement of people, goods, or information.
Density is a measure of how much mass is contained within a given volume. It is usually expressed in units of mass per unit volume, such as grams per cubic centimetre (g/cm³) or kilograms per cubic metre (kg/m³). The formula for density is:
Density = mass / volume

0 of 10 Questions completed
Questions:
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
0 of 10 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
What property of solids distinguishes them from liquids and gases?
Which type of solid has a regular and repeating pattern of particles?
What property of liquids allows them to form droplets?
What is the process by which particles move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration?
What is the measure of how much the volume of a substance decreases when subjected to an applied pressure?
What is the force exerted by gaseous particles per unit area called?
Which property of gases allows them to expand to fill any available space?
What property of gases is affected by changes in temperature and pressure?
Which property refers to the ability to move or be moved from one place to another?
What is a measure of how much mass is contained within a given volume called?