
The properties of gases are governed by the following laws.
This law was given by R.Boyles in 1662.
Boyle’s Law states that at a constant temperature, the volume of a fixed amount of gas is inversely proportional to its pressure.
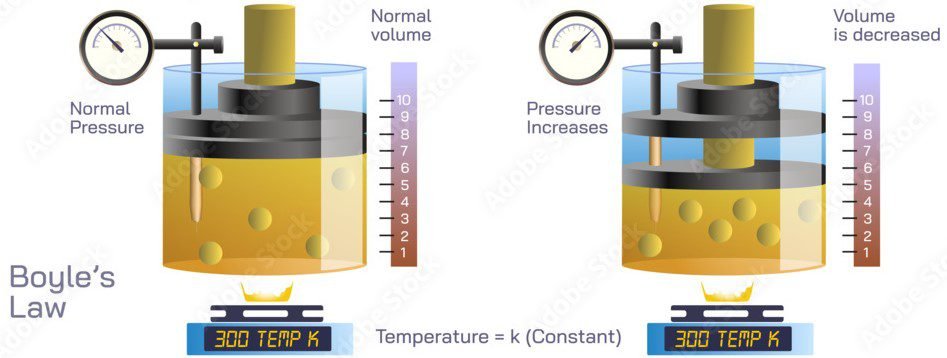
This means that if the pressure of a gas increases, its volume will decrease, and if the pressure of the gas decreases, its volume will increase, as long as the temperature remains constant. This relationship can be expressed mathematically as:
PV = k
where P is the pressure of the gas, V is its volume, and k is a constant value representing the initial conditions of the gas.
Let P be the pressure of a gas, V be its volume, and k be a constant of proportionality. Then, according to Boyle’s Law:
P ∝ 1/V
or
PV = k
To derive this expression, we start with the ideal gas law:
PV = nRT
where P is the pressure, V is the volume, n is the number of moles of gas, R is the gas constant, and T is the absolute temperature. Assuming that the amount of gas remains constant (i.e., n and R are constant), we can rewrite this equation as:
PV = kT
where k is a constant of proportionality that combines n and R. We can then rearrange this equation to isolate P:
P = kT/V
Now, if we assume that the temperature remains constant (i.e., T is constant), we can rewrite this equation as:
P ∝ 1/V
or
PV = k
This is the expression for Boyle’s Law.

0 of 10 Questions completed
Questions:
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
0 of 10 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Boyle’s Law describes the relationship between which two variables?
According to Boyle’s Law, if the pressure of a gas is doubled while the temperature remains constant, what happens to its volume?
A gas occupies a volume of 500 mL at a pressure of 1.0 atm. If the pressure is increased to 2.0 atm while the temperature remains constant, what will be the new volume of the gas
Boyle’s Law is applicable for which states of matter?
If the volume of a gas is halved while the temperature remains constant, what happens to its pressure according to Boyle’s Law?
A gas at a pressure of 2.0 atm occupies a volume of 2.0 L. If the volume is increased to 4.0 L while the pressure remains constant, what will be the new pressure of the gas?
Which graph represents the relationship between pressure and volume according to Boyle’s Law?
Boyle’s Law states that at constant temperature, the product of pressure and volume is equal to a constant. What is this constant called?
According to Boyle’s Law, if the volume of a gas is decreased while the pressure remains constant, what happens to its temperature?
Which of the following best describes Boyle’s Law?