
A plant tissue is defined as a group of similar cell to perform similar function and exhibit similar properties for example photosynthesis, transport etc.
There are two major categories of tissues in plants i.e. Meristematic tissues and Permanent tissues.
A meristematic tissue is the plant tissue that has the ability to divide actively throughout its life.
They are found at the tips (apex) and sides of roots, shoots and stem.
These are two main types of meristematic tissues in plants.

Plant tissue that has completed its growth and differentiation and is usually incapable of meristematic activity.
They originate from primary meristem.
There are two types of permanent tissues.
The simple tissue is made up of one type of cell forming a uniform or homogeneous system of cells.
Simple tissues may be further divided into following types.
The tissue which forms the outer protective covering of the plant and is represented , in the primary plant body, by epidermis is called dermal (epidermal) tissue.
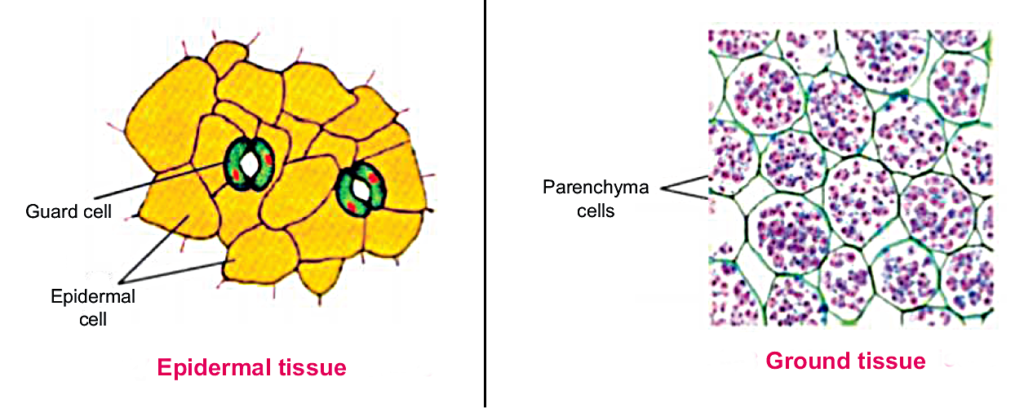
A ground tissue arises from the ground meristem, If fills in the soft parts of the plants, such as cortex, pith, pericycle, etc.
The tissues which provide strength, flexibility and structural support to plants are called supporting tissues.
They provide structural support and rigidity to the plant.
They are further classified into two types.
Collenchyma is a tissue composed of living elongated cells having unevenly thickened primary cell walls.
There are two major categories of tissues in plants i.e. Meristematic tissues and Permanent tissues.
They are mostly found in cortex of young stems, midribs of leaves and in petals of flowers.
These tissues provide structural support to plants without rejecting growth due to their relatively soft cell wall.
The sclerenchyma consists of thick and rigid secondary cell walls, often unified.
They are often found in xylem and hard fruit coats etc.

A plant tissue composed of more than one type of cell is called a compound or complex tissue.
Xylem and phloem tissues, found only in vascular plants, are examples of composed tissues.
The tissue that functions to transport water and minerals from roots to aerial parts is called xylem.
In dicot they are located inside the phloem.
Due to the presence of lignin, the secondary walls of its cells are thick and rigid with overlapping ends.
It is composed of the following elements.
The tissue that transports nutrients from leaves to various parts of plant is calledphloem. Phloem is a complex, food conducting tissue in vascular plants.
In dicot they are located outside the xylem.
Phloem is composed of four elements:
They transport food and other metabolic products from leaves to various parts of the plant.


0 of 10 Questions completed
Questions:
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
0 of 10 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
What is a plant tissue?
Which of the following is not a type of meristematic tissue?
Where are apical meristems located in plants?
What is the function of lateral meristems?
What is the main function of epidermal tissue?
Which type of plant tissue is responsible for photosynthesis?
What is the main function of xylem tissue?
Which element of phloem tissue is responsible for conducting sugars and nutrients?
What is the function of collenchyma tissue?
Which type of tissue is composed of more than one type of cell?