The process by which plants make their own organic food by taking inorganic molecules from their surroundings, in the presence of sunlight is called photosynthesis.
Formation Of Glucose
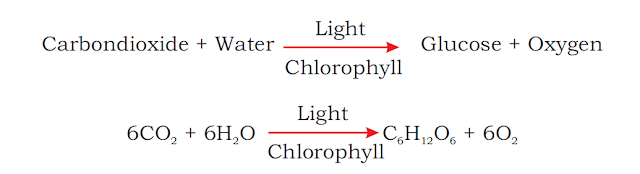
Plants can build sugar by taking CO2 from air and water from the soil, For the synthesis of sugar like glucose (C6H12O6) carbon and oxygen are provided by the atmosphere carbon dioxide whereas the water molecules provide hydrogen.
Procedure
Sunlight provides the energy which is stored in chlorophyll of the plant cells. Enzymes are also needed for this process. This process is completed in the mesophyll cells of the leaves where chlorophyll is present. In this the plants build sugar molecules from the simple inorganic compounds carbon, oxygen and hydrogen.
(i) Role Of Glucose:
The fundamental molecule produced during photosynthesis is simple sugar i.e. Glucose. Glucose utilizes in most of the metabolism of plant to produce secondary products like starch and other polysaccharides. Plants also use carbohydrates to form fats, proteins and other chemical like Nucleic Acids. This glucose is also used in respiration as reactant to produce energy for the metabolism of living organisms.
(ii) Essential In Food Chain:
Plants are not the only organisms which depend on photosynthesis but animals (Heterotrophs) also depend on phototrophs (i.e plants). Animals utilize the molecules of phototrophs as food molecules. If an animal is herbivorous it feeds directly on plants. If an animal is carnivorous it depends on herbivores (those animals which feed on plants). These feeding sequences and relationship are called Food Chains.
(iii) Role Of Oxygen:
Photosynthesis is the only process which produces free O2 by splitting water. This O2 is utilized by all living organisms for respiration to produced energy for metabolism. Without O2 living organisms cannot survive.
(iv) Quantity Of CO2 and O2 In nature Is Maintained:
During Photosynthesis plants fix CO2 and release O2 in environment. CO2 has a property to absorb heat of sun. If its quantity increases in environment, there will be increase in an environmental temperature on earth called Global warming. Thus photosynthesis keeps the quantity of CO2 to maintain the temperature of earth.

Chlorophyll is the green pigment found in the chloroplast of plant cells. It captures a specific part of visible light only, therefore it is not a reactant but absorbs energy needed to drive the reaction. In other words,Photosynthesis converts light energy to chemical energy.
Green parts of plants and algae contains special cell organelle called chloroplast.
Reaction of photosynthesis involves a number of chemical reactions which are catalyzed by a number of enzymes, either in cyclic or noncyclic ways. Each reaction occurs are different site in chloroplast limelight dependent reaction and dark independent reaction.

The whole process of photosynthesis I mainly divided into two stages
1) Light Reaction OR Light –Dependent Reaction
2) Dark Reaction OR Dark– Dependent Reaction
Light reaction is also known as light dependent reaction, as it requires light in the reaction. Chlorophyll and other molecules capture energy from light and convert some of it into chemical energy.
NADP already exists in the chloroplast reduced into NADPH2.

ADP is another compound which is present in the cell. ADP (Adenosine Triphosphate) reacts with the phosphate group by using the light energy to form ATP.
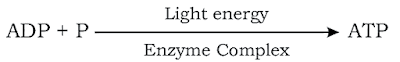
Dark reaction is also known as the light independent reaction because light energy is not captured during this phase of photosynthesis.
NADPH2 and ATP are the two energy rich compounds which are formed during the light reaction. These compounds provide energy for the combination of CO2 and H2O to synthesise glucose. Fixation of CO2 and its conversion into glucose occurs in the chloroplast by means of a series of reactions known as Calvin cycle of dark reactions. In this stage of photosynthesis glucose molecules are formed and stored in the chloroplast such as starch.
Any environment factor’s absence or deficiency of which can decrease the rate of a metabolic reaction is called the limiting factor.
Many factors act as limiting factors for photosynthesis.
i Light Intensity
ii Temperature
iii Carbon Dioxide
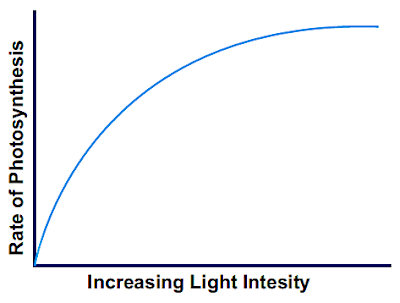
The rate of photosynthesis varies with light intensity .It decreases as the light intensity and increases as the intensity increases. However at much higher light intensity, the rate of photosynthesis becomes constant.
The rate of photosynthesis decreases with decreases in temperature. It increases as the temperature is increased over a limited range. But if light intensity is low, increasing the temperature has little influence on the rate of photosynthesis.

Carbon dioxide concentration raises the rate of photosynthesis, it goes on increasing until limited by the factors. Increases in CO2 concentration beyond a certain level causes the closure of stomata and it decreases the rate of photosynthesis.

0 of 10 Questions completed
Questions:
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
0 of 10 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
What is photosynthesis?
What are the reactants in the process of photosynthesis?
What is the role of chlorophyll in photosynthesis?
Which organelle in plant cells is responsible for photosynthesis?
What are the two stages of photosynthesis?
Where does the light reaction of photosynthesis take place?
What are the products of the light reaction in photosynthesis?
Which phase of photosynthesis does not require light?
What are the limiting factors of photosynthesis?
How does the rate of photosynthesis change with increasing carbon dioxide concentration?