
It is a type of cell division in which a parent cell is divided into four daughter cells each having half the number of chromosomes as contained in the parent cell. Meiosis is completed in two stages and occurs in germ cells.
Meiosis consists of two successive divisions of a mother cell. The first division is a reduction division in which the number of chromosomes reduces to half while the second division is just like mitosis. Each meiotic division is further divided into four phases.

Following events takes place in first meiotic division.
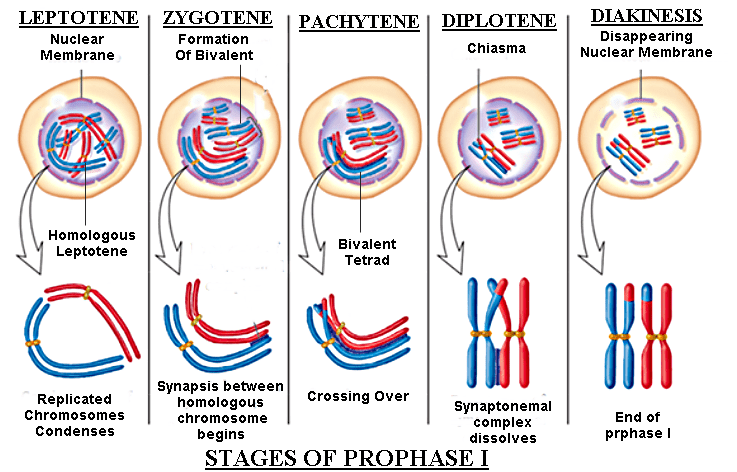
The prophase I is the longest phase of meiosis and it’s divided into the followingSub-stages.
In this stage, chromosomes appear to be thin, long thread-like and longitudinally single.
During this stage, homologous chromosomes move towards each other and become ultimately associated to form bivalents. This process of pairing of homologous chromosomes is called synapsis.
During this stage, the paired chromosomes of each bivalent get shortened and thickened. Homologous chromosomes get coiled around each other and each starts splitting longitudinally to form four chromatids called Tetrad.
During this stage, chromosomes uncoil and get separated. This separation isincomplete and paired chromosomes are in contact with each other at one or more points called Chiasmata.
During uncoiling exchange of chromosome parts occurs. This exchange is called Crossing over.
During this sub-stage, the nuclear membrane and nucleus disappear.The separation of bivalents is completed by the process of terminalization, by which chiasmata move from centromere towards the ends of chromosomes like a zipper.
During this stage, bivalent is arranged at equatorial plane, and each attach itself to the half spindle fibers.
In the contraction, of spindle fibers result in movement of each chromosome of homologous pairs towards the opposite. Hence two sets of chromosomes are formed at opposite poles of the cell.
Now, a nuclear membrane is formed around each set of chromosomes and the nucleolus reappears.


The second meiotic division is actually mitotic division which divides each haploid cell formed during meiosis I into two daughter haploid cells.
The second meiotic divisions include.
During this stage, centrioles divides and spindle are formed at right angles to the spindle of first meiotic division. Nuclear membrane disappears and chromosomes split.
Each split chromosome sets arrange themselves at the equatorial plane. Each chromosomes attach themselves to half spindle fibers.
Contraction of spindle fibers results in separation of chromatids and two sets of chromosomes are formed. Each set of chromatids (monads) move towards the pole.
In this phase, the nuclear membrane and nucleolus reappear forming two nuclei. Telophase is followed by cytokinesis.


| Cell Type | Description | Cell Division Type |
|---|---|---|
| Somatic Cells | Cells which form the body of organisms | Mitosis |
| Germ Line Cells | Cells which give rise to gametes | Meiosis |
Mitosis plays an important role in the life of an organism. It is responsible for development and growth of organisms by increasing exact copies of cells.
As a result of meiosis, gametes are formed, each of which possess a haploid number of chromosomes. At the time of fertilization, chromosome number becomes diploid. Thus, meiosis helps in maintaining the chromosome number in species generation after generation.
During the process of meiosis, crossing over takes place, which results in new combination of genetic materials.
Meiotic error is a mistake or abnormality that occurs during the process of meiosis, which is the cell division process that produces gametes (sex cells) such as sperm and egg cells. Meiotic errors can occur during various stages of meiosis and can result in chromosomal abnormalities in the resulting gametes.
One common type of meiotic error is called nondisjunction, which occurs when chromosomes fail to separate properly during meiosis, leading to an uneven distribution of chromosomes in the resulting gametes. This can result in gametes with too many or too few chromosomes, which can lead to genetic disorders in offspring if fertilization occurs with an abnormal gamete.
Other types of meiotic errors include chromosome translocations, inversions, and deletions, which can also lead to genetic disorders. It is important to note that meiotic errors can occur randomly and are not always caused by external factors or genetic predisposition.

0 of 8 Questions completed
Questions:
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
0 of 8 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Meiosis is a type of cell division that results in the formation of:
During which phase of meiosis do homologous chromosomes pair up and undergo crossing over?
What is the significance of crossing over in meiosis?
What happens during anaphase I of meiosis?
How many divisions occur in meiosis?
What is the ploidy of the daughter cells produced at the end of meiosis?
Meiosis is important for:
What is a common type of meiotic error?