
Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from a neutral atom or molecule in the gas phase.
It is measured in KJ/mol.
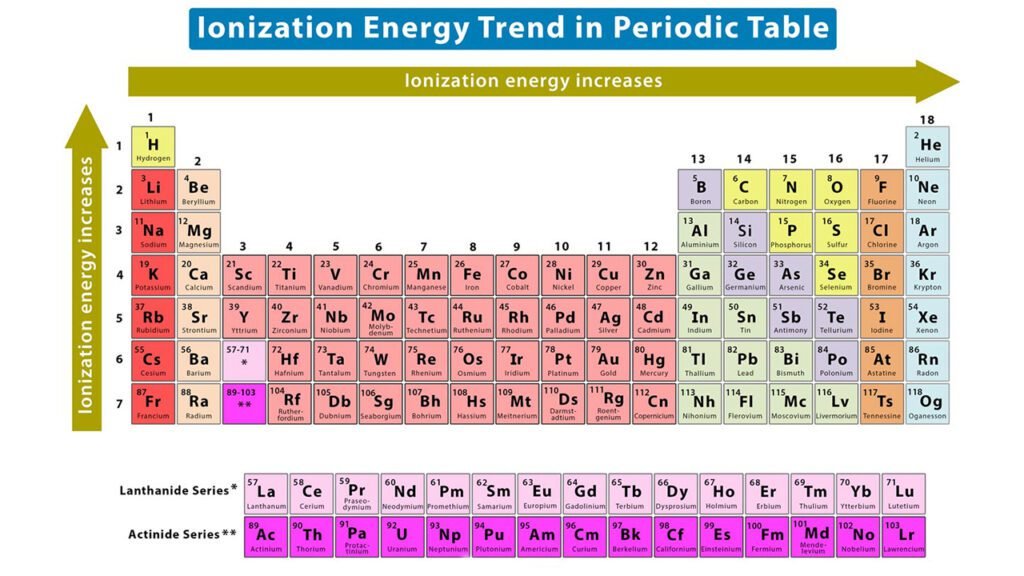
The Ionization energy tends to increase as you move from left to right across a period in the periodic table, since the nuclear charge increases while the number of energy levels remains the same. This means that it becomes more difficult to remove an electron from the atom.
The Ionization energy tends to decrease as you move down a group in the periodic table, since the distance between the electrons and the nucleus increases. This makes it easier to remove an electron from the atom.

0 of 10 Questions completed
Questions:
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
0 of 10 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
What is the primary factor contributing to the increase in electron affinity across a period in the periodic table?
Which unit is typically used to measure electron affinity?
What is the general trend of electron affinity when moving from left to right across a period?
What is the primary factor contributing to the decrease in electron affinity down a group in the periodic table?
What is the definition of electron affinity?
Which group of elements is expected to have the highest electron affinity?
What is the shielding effect?
What is the primary factor contributing to the increase in electron affinity across a period?
Which statement accurately describes the relationship between electron affinity and ionization energy?
Which element is known to have the highest electron affinity?