
The dipole moment,µ ,is defined as the product of the distance, d, separating charges of equal magnitude and opposite sign, and the magnitude of the charge, q.
µ = d × q
When hydrogen (H) is covalently bonded to a highly electronegative atom X (O, N, F), the shared electron pair is pulled so close to X that a strong dipole results.
Since the shared pair is removed farthest from the H atom , its nucleus (the proton) is practically exposed. The H atom at the positive end of a polar bond nearly stripped of its surrounding electrons, exerts a strong electrostatic attraction on the lone pair of electrons around X in a nearby molecule. Thus:
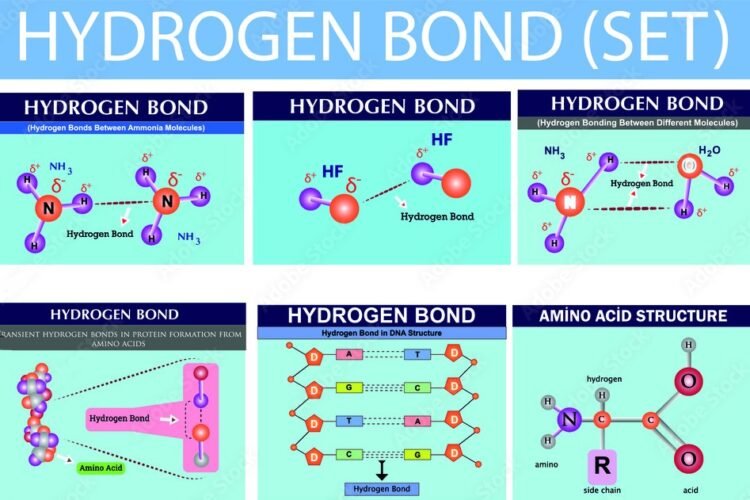
“The electrostatic attraction between an H atom covalently bonded to a highly electronegative atom X and a lone pair of electrons of X in another molecule, is called Hydrogen Bonding.” Hydrogen bond is represented by a dashed or dotted line.

In NH3 molecules, there are three H atoms covalently bonded to the highly electronegative N atom. Each H atom can hydrogen bond to the N atom of other molecules or other electron efficient atom of any other neighboring molecule.


0 of 10 Questions completed
Questions:
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
0 of 10 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
The dipole moment is defined as the product of:
Hydrogen bonding occurs when hydrogen is covalently bonded to:
Hydrogen bonding is characterized by:
Which of the following atoms is NOT capable of forming hydrogen bonds?
Hydrogen bonds are longer and weaker than:
The preferred bonding direction of hydrogen bonding is attributed to:
In which of the following molecules can hydrogen bonding occur?
The hydrogen bonds in water (H2O) form chains or clusters due to the:
Ammonia (NH3) can form hydrogen bonds with other ammonia molecules through:
Hydrogen bonding is an important factor contributing to the unique properties of substances such as: