It is a system which comprises a complex series of various organs and digestive glands which work in coordinate with each other to carry out a function of the digestion of food.
Digestion is a process in which large and non-diffusible molecules of food are converted into smaller and diffusible molecules by the action of enzymes.
Digestive system consists of two parts.
The alimentary canal is divided into
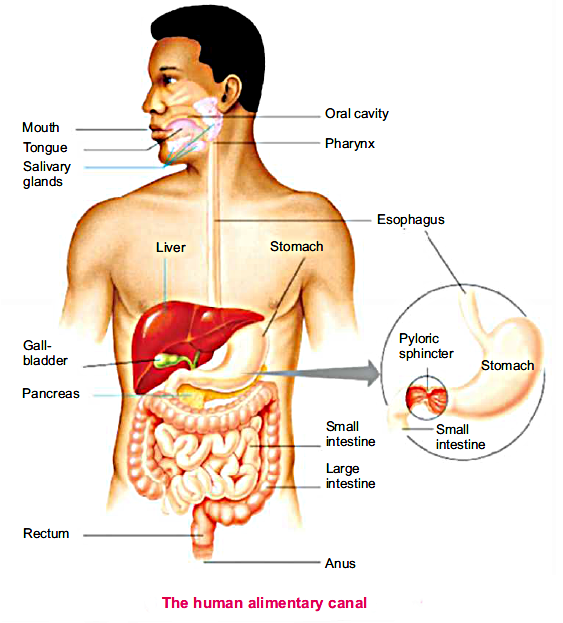
It is the first part of the alimentary canal. It is equipped with four kinds of teeth. Oral cavity or mouth also contains three pairs of ordinary glands which produce saliva.
The function oral cavity are given below
In oral cavity food is selected or rejected due to taste, hard object or diet.
The second function of the oral cavity is the grinding of food by teeth. It is known as chewing or mastication. Grinding increases the surface area of food.
The salivary glands of the oral cavity secrete which lubricates the food. It adds water and mucus to the food.
Saliva also contain an enzyme, salivary amylase, which helps in the semi digestion of staid partially.
Swallowing is accomplished by muscles movement by the tongue and mouth, food moves into the throat of the pharynx.
The pharynx is a passage for food and air, is about 5 inches (12.7 centimetres) long thick and muscular part of alimentary canal is present at the posterior end of the oral cavity.
The bolus from the oral cavity is pushed into the oesophagus through the pharynx. A flexible lap of tissue called the epiglottis reflexively closes over the windpipe which we swallow to prevent choking.
The oesophagus is a muscular tube which connects the pharynx to the stomach.
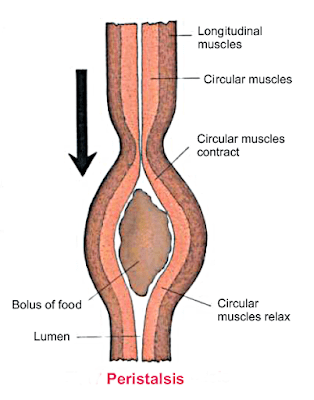
Peristalsis is the movement of food from the oral cavity to the rectum.
The wave of contraction & relaxation in the smooth muscles of the alimentary canal wall is called Peristalsis.
Stomach is a dedicated part of the alimentary canal. It is J-shaped and in the left of the abdomen, just beneath the diaphragm.
Stomach has two main portions.

Cardiac portion is present immediately after the oesophagus
Pyloric portion is located beneath the cardiac end.
Sphincters are the openings which are guarded by muscles and the stomach has two sphincters.
Cardiac sphincter is between the stomach and oesophagus. Bolus enters stomach from oesophagus through cardiac sphincter
Secretion of gastric gland is known as gastric juice. Gastric juice is composed chiefly of:
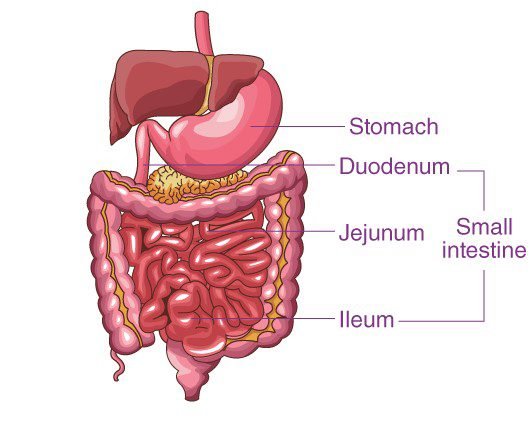
This is a long narrow tube in the form of coded loofs. It is differentiated into three distinct parts
It is C-shaped first part of small intestine about10 inches (25cm) of small intestine where most of the digestive process occurs
In the small intestine food is further mixed with secretions from the pancreas and liver.
Bile juice from the gallbladder first neutralises the audi chyme to facilitate digestion and also emulsifies fats.
Pancreatic juice from pancreas contains three enzymes.
It is the coiled mid-section about 2.4 metres long after duodenum.
It is concerned with the rest of the digestion of protein, carbohydrates and lipids.
It is relatively long and more coiled tube which is about 3.6 metres in length and receives completely digested food from jejunum.
The rest of the digestion is completed in the ileum. The walls of the small intestine house glands which produce intestinal juices; this juice has enzymes aminopeptidase and disaccharidases.
It converts the peptides into amino acids.
Lactose or sucrose is converted into glucose by the action of disaccharides.
On the internal walls of the ileum these are very fine finger-like projections called villi. Inside each villus there is a rich supply of blood capillaries forming a network. There is also a single lymph vessel called lacteal. Digested food is absorbed in it. Besides fatty acids all the nutrients diffuse through the surface cells of villi and are taken into the blood flowing in blood capillaries. These capillaries gain together to form large blood vessels called hepatic portal vein which carries the absorbed food to liver, while fatty acid absorbed by the surface cells of villi rejoin together to form fats which are passed into lacteals of villi join together to form lymph vessels, which form a lymphatic system to deliver these fats into blood stems.

The small intestine opens into large intestine which is a comparatively wide tube is subdivided into following regions.
The caecum is a pouch at the beginning of the large intestine that joins the small intestine to the large intestine. A small hollow, finger like pouch, hangs at the end of the caecum call appendix.
The colon extends from the caecum and three parts.
Rectum is the terminal part of large intestine where faeces are stored until they leave all digestive systems through the anus.

In human digestive system secretes digestive chemicals & enzymes which being out the process of digestion.
Liver is the largest gland in the body. It is a reddish brown gland that is located in the abdomen behind the diaphragm more towards the right side.

It is a leaf-like organ that lies behind the stomach horizontally within the curve of duodenum.
It acts on starch to break it down into maltose.
It converts the proteins into smaller peptides.
It breaks fat droplets into fatty acids and glycerol.
| Name of digestive juice | Source | Secretion/Enzyme | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Saliva | Salivary glands in oral cavity | Ptyalin | Breaks down starch into maltose |
| Gastric Juice | Gastric glands in stomach | HCI, Pepsin, Renin | Germicidal activities; pepsin breaks down proteins into peptones, curdles milk |
| Bile | Liver | Nil | Turns acidic chyme alkaline and emulsifies fat |
| Pancreatic juice | Pancreas | Trypsin | Breaks down proteins into peptides |

0 of 6 Questions completed
Questions:
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
0 of 6 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
What is the process of converting large food molecules into smaller molecules by the action of enzymes called?
Which of the following is NOT part of the alimentary canal?
What is the function of the oral cavity in the digestive system?
Which part of the digestive system is responsible for the peristaltic movement?
What is the function of the gastric juice in the stomach?
Which part of the small intestine is responsible for the digestion of most nutrients?