
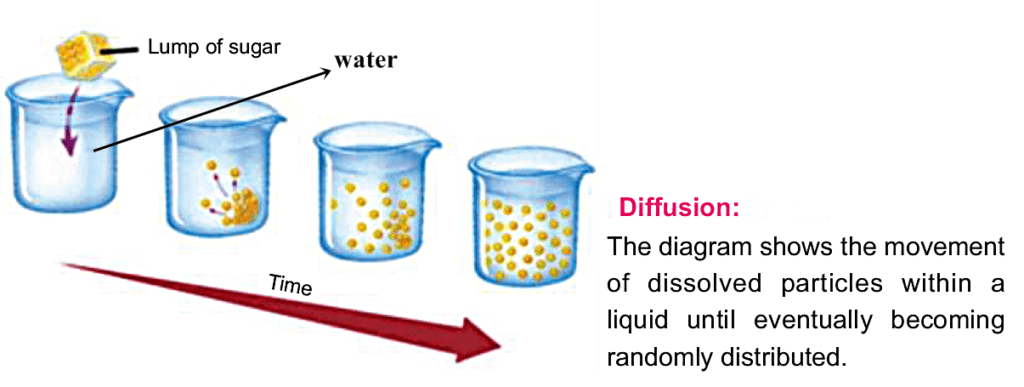
Diffusion if the movement of molecules from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration. It is therefore said to occur down a concentration gradient.
Osmosis is the movement of water molecules down a concentration gradient i.e. from dilute solution to concentrated solution.

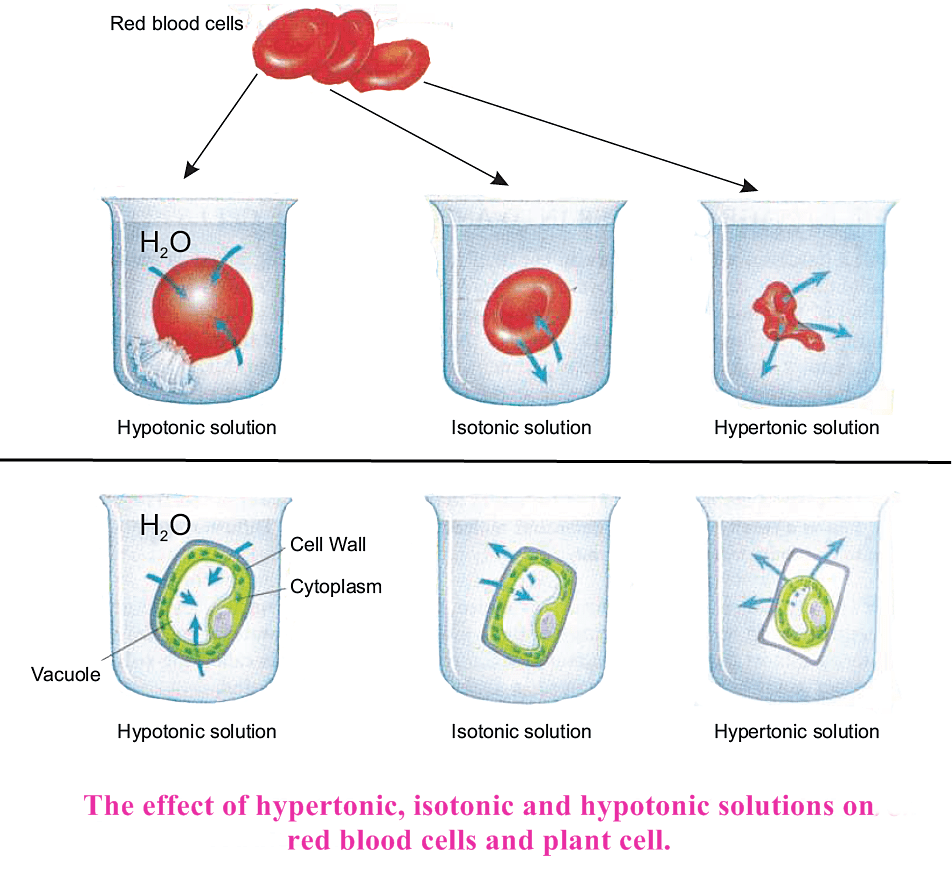
The term tonicity is defined as the relative concentration of solutes in the solutions being compared.
On the basis of tonicity, there are three types of solutions.
A hypertonic solution is defined as a solution that has relatively more solute than its surroundings or compared solution.
A hypotonic solution has relatively less solute than its surroundings or compared solution.
Isotonic solution is defined as a solution which has equal amount of solute to its urroundings or compared solutions.
Facilitated diffusion is the rapid exchange of specific molecules by the means of a special carrier protein.

0 of 8 Questions completed
Questions:
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
0 of 8 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
What is diffusion?
Which process involves the movement of water molecules down a concentration gradient?
What is the importance of osmosis in animal and plant cells?
Which solution has a higher concentration of solute compared to its surroundings?
Which type of solution has relatively less solute than its surroundings?
What is facilitated diffusion?
What is the form of energy used in active transport?
Which example represents active transport?