
Covalent bond is a bond formed when two atoms share one or more electron pairs. Each atom contributes an equal number of electrons towards the bond formation.
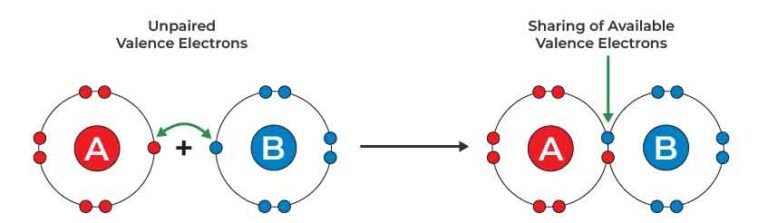
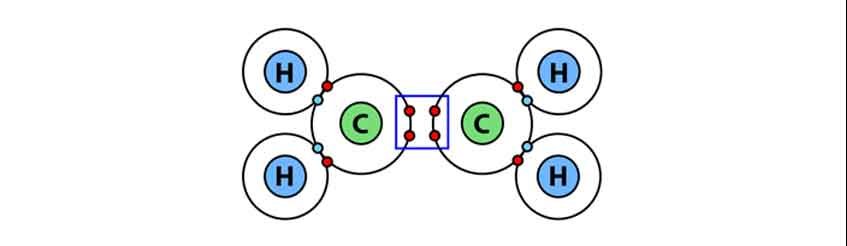
The covalent bond is formed by mutual sharing of electrons between two atoms. The electrons that pair up to form a chemical bond are called ‘bond pair’ electrons. Depending upon the number of bond pairs, covalent bond is classified into following three types:

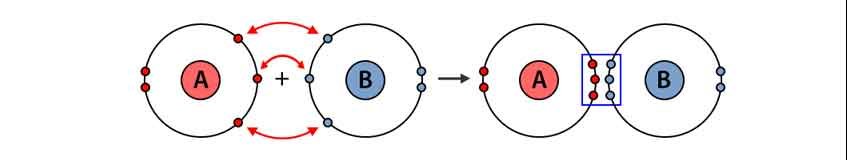
When covalent bond is formed between two dissimilar atoms. is known as a polar covalent bond, characterised by a partial positive charge on one atom and a partial negative charge on the other.
EXPLANATION:
For example, the electrons in the H–Cl bond of a hydrogen chloride molecule spend more time near the chlorine atom than near the hydrogen atom. Thus, in an HCl molecule, the chlorine atom carries a partial negative charge and the hydrogen atom has a partial positive charge. Figure below shows the distribution of electrons in the H–Cl bond. We sometimes designate the positive and negative atoms in a polar covalent bond using a lowercase Greek letter “delta,” δ, with a plus sign or minus sign to indicate whether the atom has a partial positive charge (δ+) or a partial negative charge (δ–). This symbolism is shown for the H–Cl molecule.

or H δ+ –––––– Cl δ-

0 of 10 Questions completed
Questions:
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
0 of 10 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Covalent bonds are formed when atoms:
In a covalent bond, atoms share:
A single covalent bond is formed by the sharing of:
Which of the following molecules contains a single covalent bond?
A double covalent bond involves the sharing of:
Which molecule exhibits a triple covalent bond?
A polar covalent bond is formed between:
In a polar covalent bond, which atom carries a partial negative charge?
Which Greek letter is commonly used to symbolize partial charges in a polar covalent bond?
In the H-Cl molecule, which atom carries a partial positive charge?