
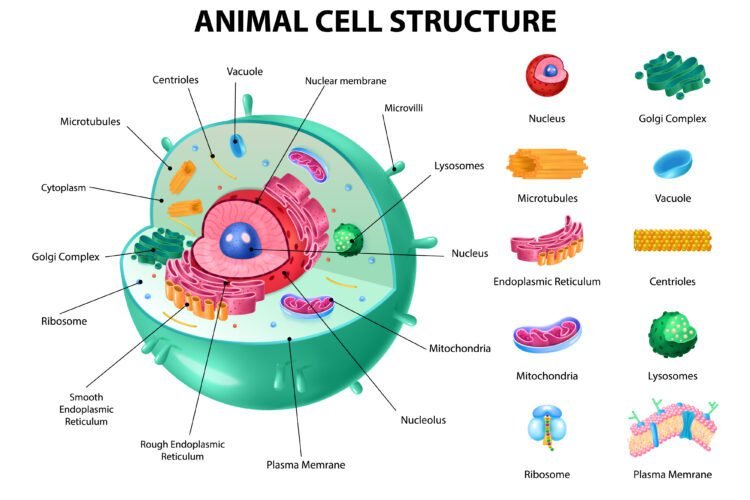
It is the fundamental unit of structure and function in all living organisms.
The openings in the cell wall are plasmodesmata that contain strands of cytoplasm that connect adjacent cells.
It is the process in which cytoplasm of the cell shrinks due to the loss of water when placed in a hypertonic condition.
The nucleus is filled with a gel-like granular fluid called nucleoplasm which has a nucleoli and chromatin network.
It is a dense connective tissue that protects joints and bones.
The streaming movement of the cytoplasm is called cyclosis.
Golgi bodies consist of a stack of flat, membrane-bound sacs called cisternae.
It is the process by which cells get rid of large molecules of waste products or toxins.
It is a small structure within a cell, consisting of liquid enclosed by a lipid layer.

0 of 10 Questions completed
Questions:
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
0 of 10 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
What is the fundamental unit of structure and function in all living organisms?
What are the openings in the cell wall that contain strands of cytoplasm connecting adjacent cells?
What is the process in which the cytoplasm of a cell shrinks due to the loss of water when placed in a hypertonic condition?
What is the gel-like granular fluid filled in the nucleus of a cell called?
What is the physiological or medicinal removal of toxic substances from a living organism called?
What is the dense connective tissue that protects joints and bones called?
What is the streaming movement of the cytoplasm called?
What are the flat, membrane-bound sacs that make up Golgi bodies called?
What is the process by which cells get rid of large molecules of waste products or toxins?
What are small structures within a cell, consisting of liquid enclosed by a lipid layer?