
“The scientific method used to solve biological problems is called the biological method.”
OR
“The scientific method in which biological problems are solved is called the biological method.”
In order to resolve a specific biological problem, biologists take the following steps.
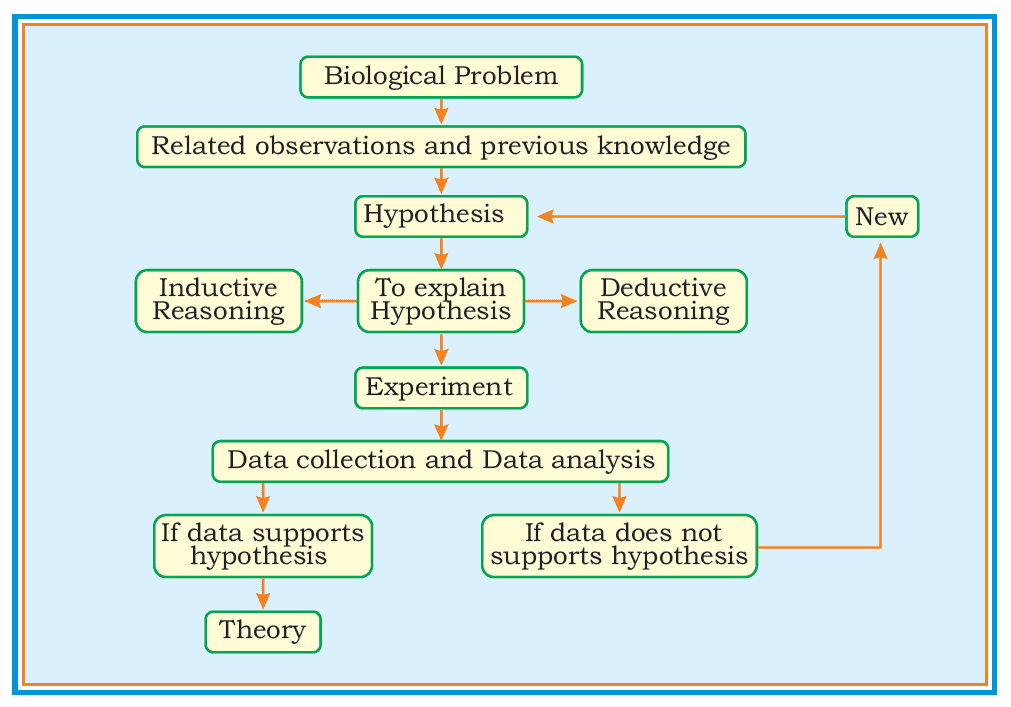
The first step is to observe the problem and formulate a question about what has been observed. Thus,
“An observation is a statement of knowledge gained through the senses (qualitative) or through the use of scientific equipment (quantitative).”
For example, in 1880, a French physician named LAVERAN studied a blood sample of a malaria patient under a microscope and observed tiny creatures in it, whom he named Plasmodium.
Biologists collect information about the problem and formulate the hypothesis by using a reasoning process i.e.
a) Inductive reasoning: moves from specific to general e.g., Shark is a fish. All fishes have scales therefore sharks also have scales.
b) Deductive reasoning: moves from general to specific. It is based on “if then” statement. Deductive reasoning can be tested and verified by experiments. For Example: In malaria case, the following deduction is made:
Experiments are designed to test the deduction. Biologists perform experiments to test the hypothesis and see if it is true or not.
The results include all observations and data made during the experiment. Results are used to confirm or reject the hypothesis.
A theory is a well-substantiated explanation of some aspect of the natural world that is based on a large body of facts that have been repeatedly confirmed through observation and experimentation.

Data can be defined as a single piece of information such as names, dates or values made from observations and experiments.
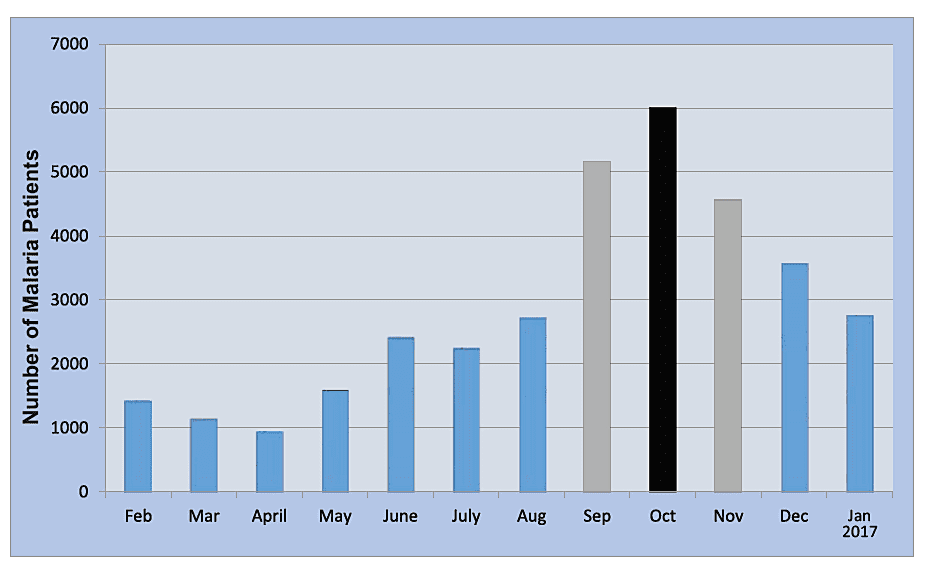
In order to formulate and then to test the hypothesis, scientists collect and organize data. Prior to conducting an experiment, it is important for a scientist to document the collection methods. Data is organized in different formats like graphics, tables, flowcharts, maps and diagrams.
Data analysis is necessary to prove or disprove a hypothesis by experimentation. It is done through the application of statistical methods.

0 of 8 Questions completed
Questions:
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
0 of 8 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
What is the biological method?
What is the first step in solving a biological problem?
What is a hypothesis?
What are deductions in the biological method?
What is the purpose of experiments in the biological method?
What is the final step in solving a biological problem?
What is data organization in the biological method?
Why is data analysis important in the biological method?